Verify a Smart Contract using the Rootstock Explorer
Contract verification is essential in the Rootstock ecosystem. It allows Rootstock Explorer users to inspect and validate the source code of deployed smart contracts.
The Rootstock Explorer provides a transparent view of the Rootstock blockchain, showing transactions, blocks, and deployed contracts. This transparency, enabled by verification, builds trust and understanding in decentralized applications.
Key reasons for verifying a smart contract
- Builds trust:
- Verification allows anyone to see the source code of a deployed smart contract, which fosters trust with users and the community.
- Increases transparency:
- Users can audit the code to confirm it performs the actions it claims to, providing confidence in the contract's operations.
- Aids in security:
- By making the code public, it can be reviewed for vulnerabilities, though users should still conduct their own security assessments.
- Enables proper tooling:
- Many development and analysis tools, such as those from Tenderly, require the contract's source code to be verified to function correctly.
- Provides public interaction:
- Verification allows users to interact with the contract on the Rootstock Explorer.
- Confirms code integrity:
- The verification process proves that the bytecode on the blockchain was generated from a specific, known source code, ensuring the contract hasn't been tampered with.
- Helps with compliance:
- Verification is essential for meeting certain compliance and regulatory requirements.
What does verification do?:
- Adds a Verified badge to the contract page, confirming that the published source code matches the deployed bytecode.
- Enables human-readable interaction with the contract — allowing users to view and call its functions directly.
- Allows downloading the contract's Application Binary Interface (ABI).
Prerequisites
- Address of the deployed contract on Rootstock.
- Complete source code of the contract.
- Compiler details:
- Solc (Solidity Compiler) version.
- Number of optimization runs.
- Constructor parameters (if applicable).
- Library addresses (if used).
In summary, this guide will help you verify your smart contract, allowing you to leverage these benefits and contribute to a more transparent and trustworthy decentralized environment on Rootstock.
Getting Started
- To start the verification process, visit the Rootstock Explorer Testnet or Rootstock Explorer Mainnet, and find your contract using the search field.
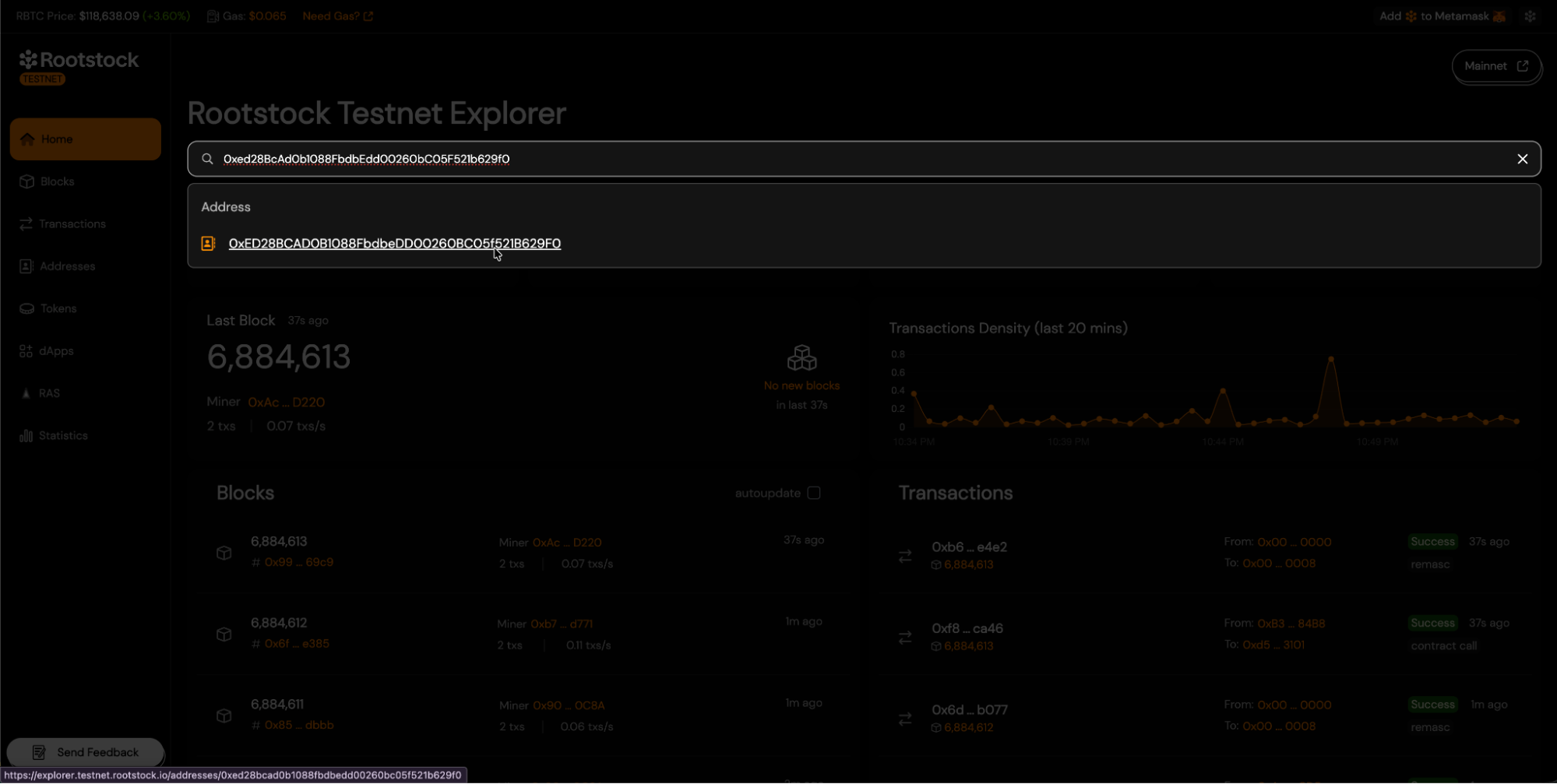
- Once you reach your contract's address view, navigate to the "Contract" tab and click the "Verify Contract" button.
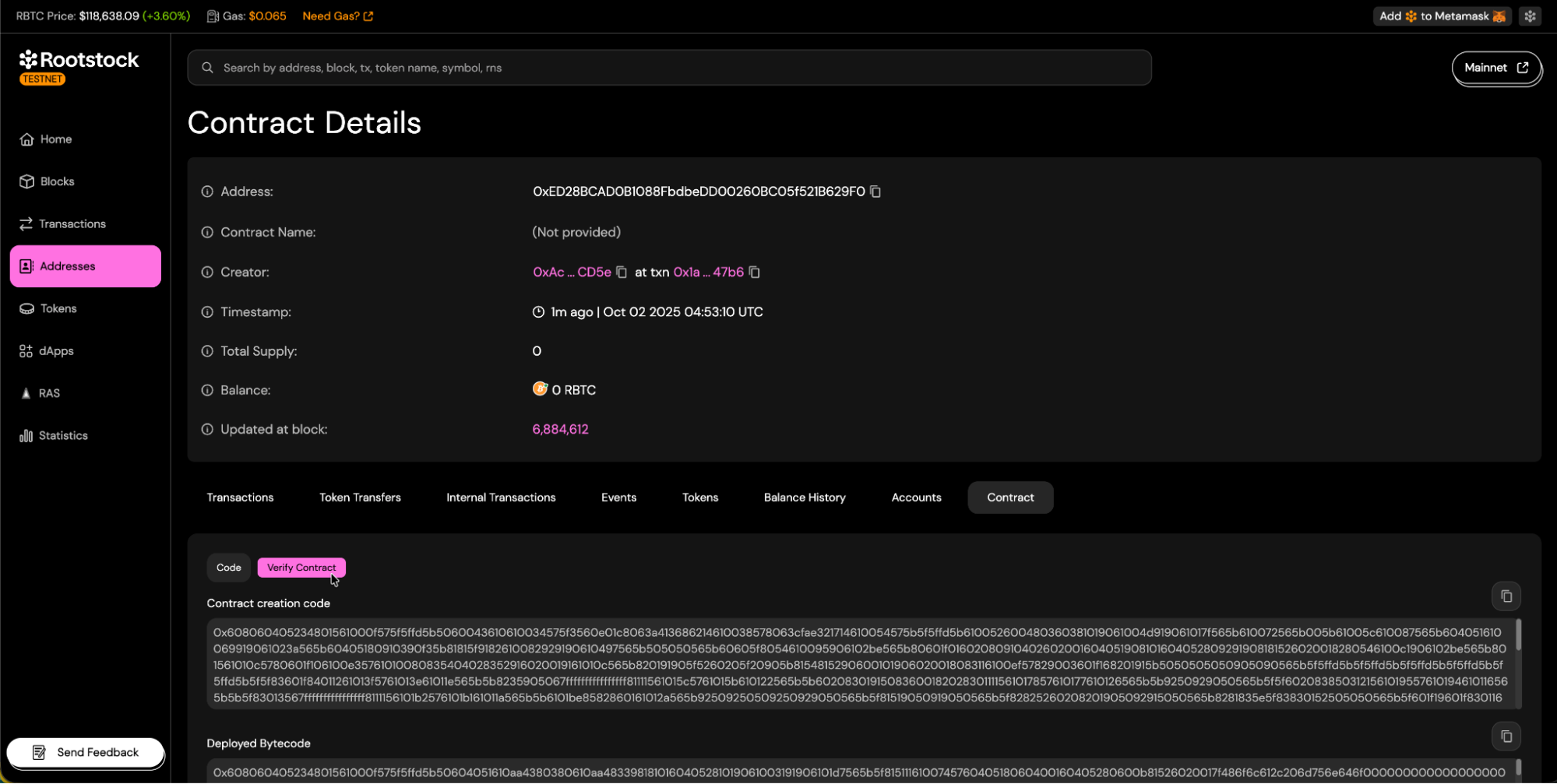
Choosing a Verification Method
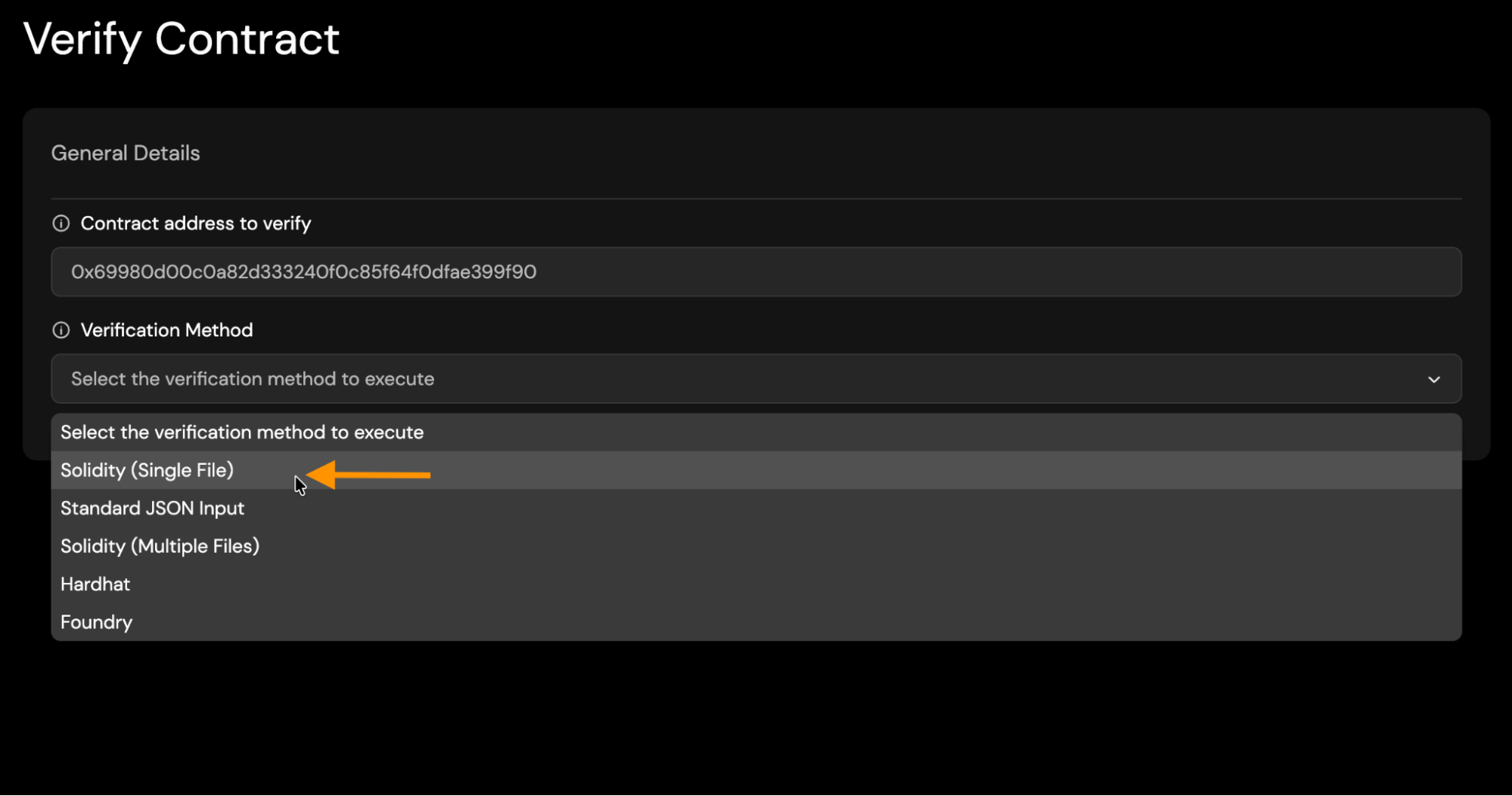
Rootstock Explorer offers 5 main methods for contract verification:
1. Single File
The Solidity (Single File) method is intended for verifying contracts that exist entirely within a single .sol file, or where the developer has already flattened all imports into one file. This method recompiles the provided contract and compares the resulting bytecode to the deployed contract on Rootstock.
Follow the steps below to successfully complete the verification process.
-
Select Solidity (Single File) Method:
-
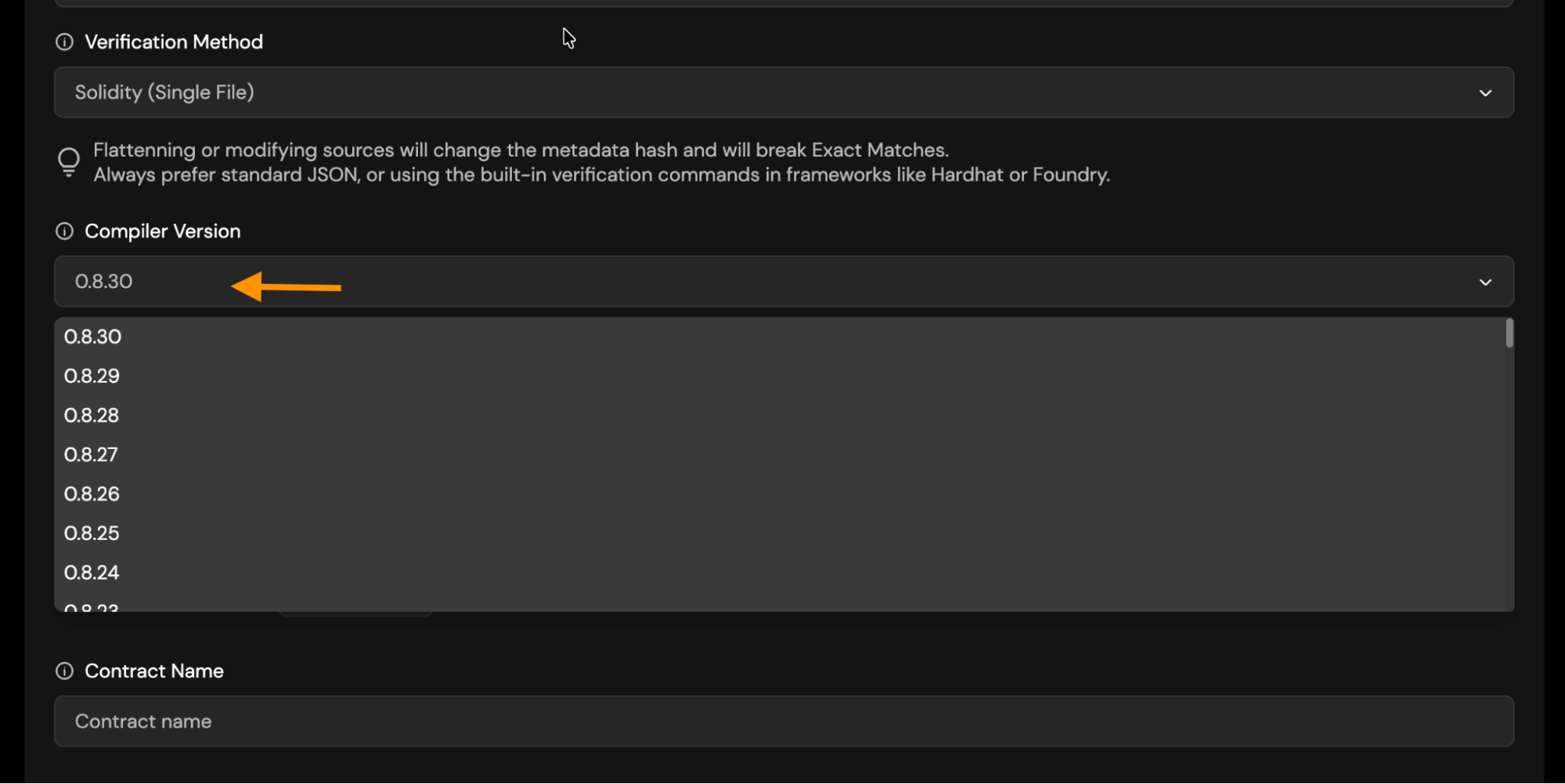
Solc Version: Choose the Solc version you used to compile your contract.
-
EVM Version: Choose the appropriate EVM version.
-
Optimization:
Runstells the Solidity optimizer how many times your contract will be executed. You must use the same runs value in verification that you used when compiling.- If you used optimization run when compiling/deploying, enable it during verification and set the same runs (default 200).
- If you didn’t use optimization, leave it disabled and don’t enter any runs.
-
Contract Name: Enter the exact name of the contract you deployed. This is required so the verifier can match the correct bytecode.
-
Paste/Upload source code: Provide the full Solidity source file.
You may choose between:
-
Paste code: Paste the raw contract source code into the field. This must be the exact source used during deployment.
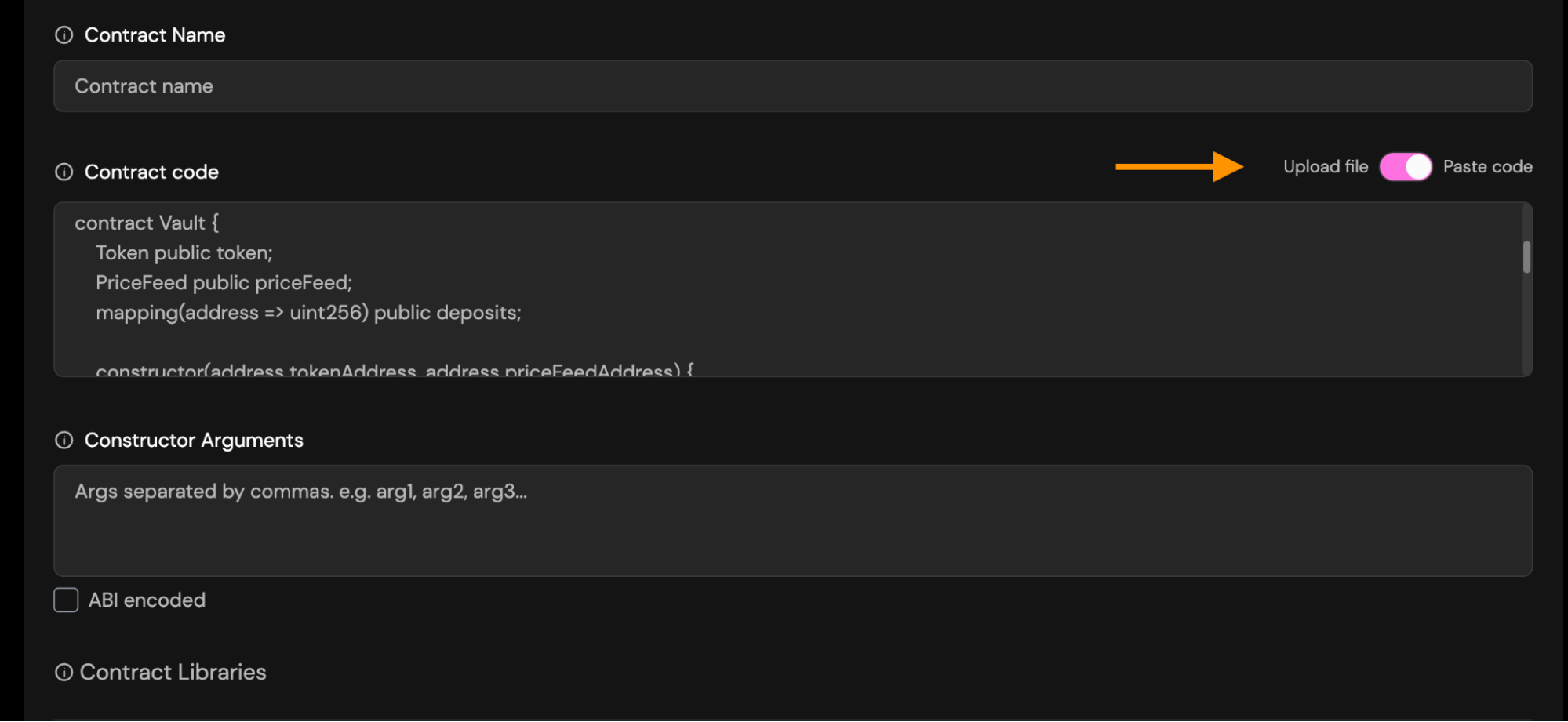
-
Upload file: Upload a
.solfile directly from your computer.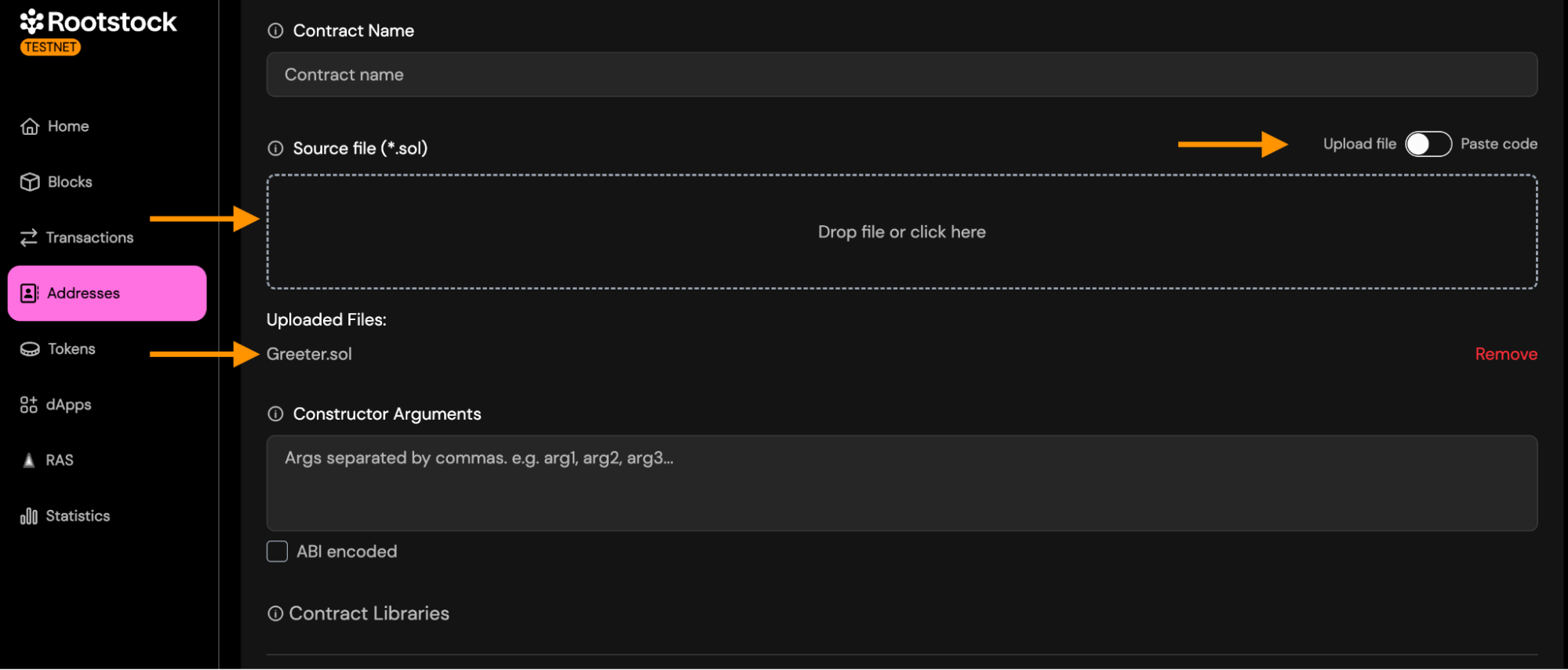
-
-
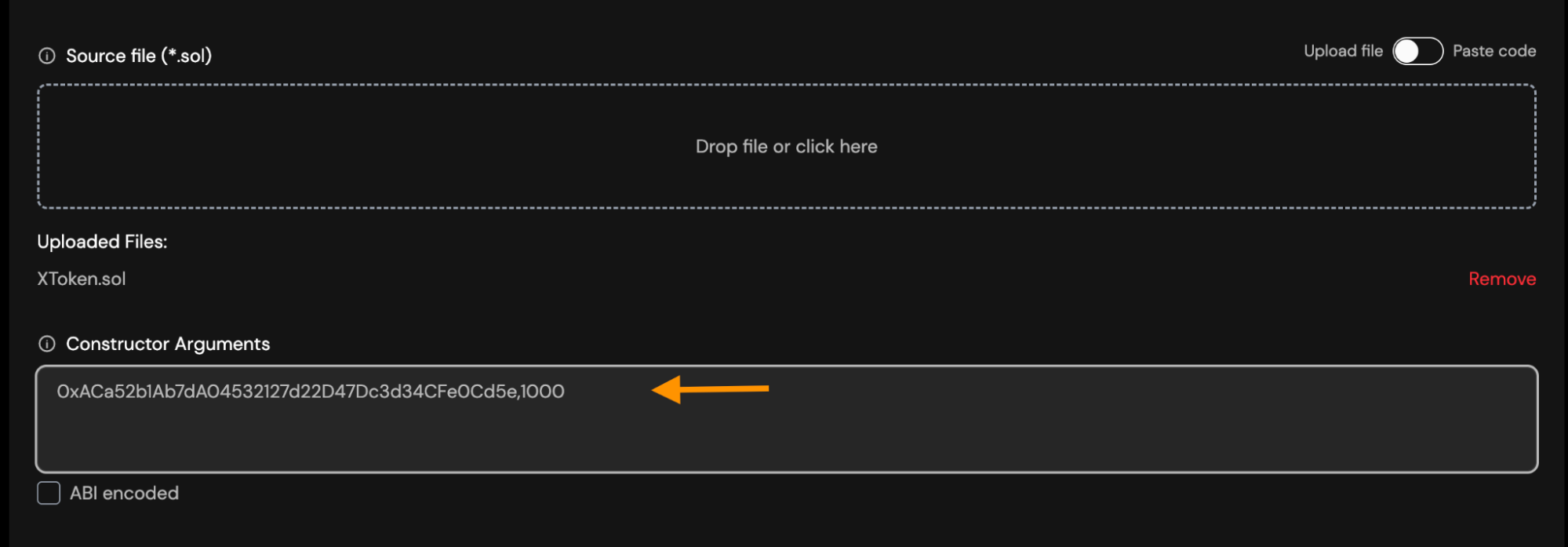
Constructor Arguments: You must enter constructor arguments separate by comma if you have more than one.
- Suppose your Solidity constructor looks like this:
constructor(address owner, uint256 maxSupply)- To verify the contract, enter the arguments like this:
0xACa52b1Ab7dA04532127d22D47Dc3d34CFe0Cd5e,1000Example:
- If you already have them in ABI-encoded format, enable the “ABI encoded” checkbox and paste the encoded string instead.
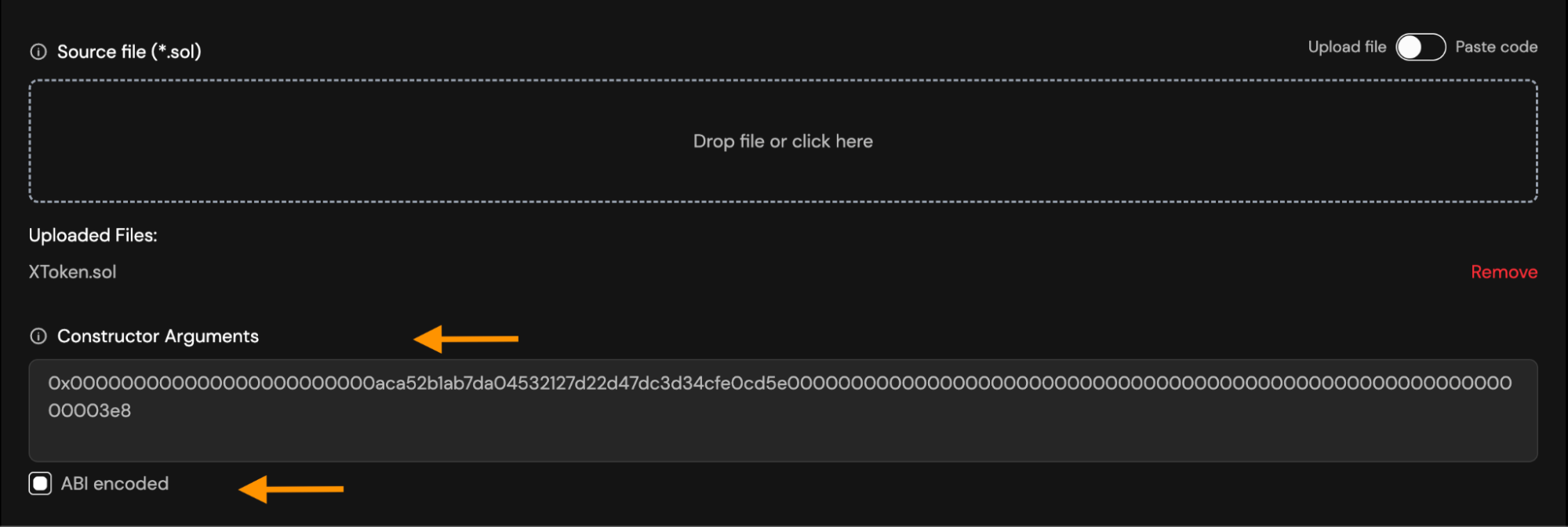
-
How to encode arguments:
- ABI-ENCODING with Ethers.js
import { AbiCoder } from "ethers";
const coder = AbiCoder.defaultAbiCoder();
const encoded = coder.encode(
["address", "uint256"],
["0xaca52b1ab7da04532127d22d47dc3d34cfe0cd5e","1000"]
);
console.log(encoded);Result:
0x000000000000000000000000aca52b1ab7da04532127d22d47dc3d34cfe0cd5e00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003e8- ABI-ENCODING from Remix:
- Open remix - Console
- Paste
web3.eth.abi.encodeParameters(
["address", "uint256"],
["0xaca52b1ab7da04532127d22d47dc3d34cfe0cd5e", "1000"]
)Result:
0x000000000000000000000000aca52b1ab7da04532127d22d47dc3d34cfe0cd5e00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003e8 -
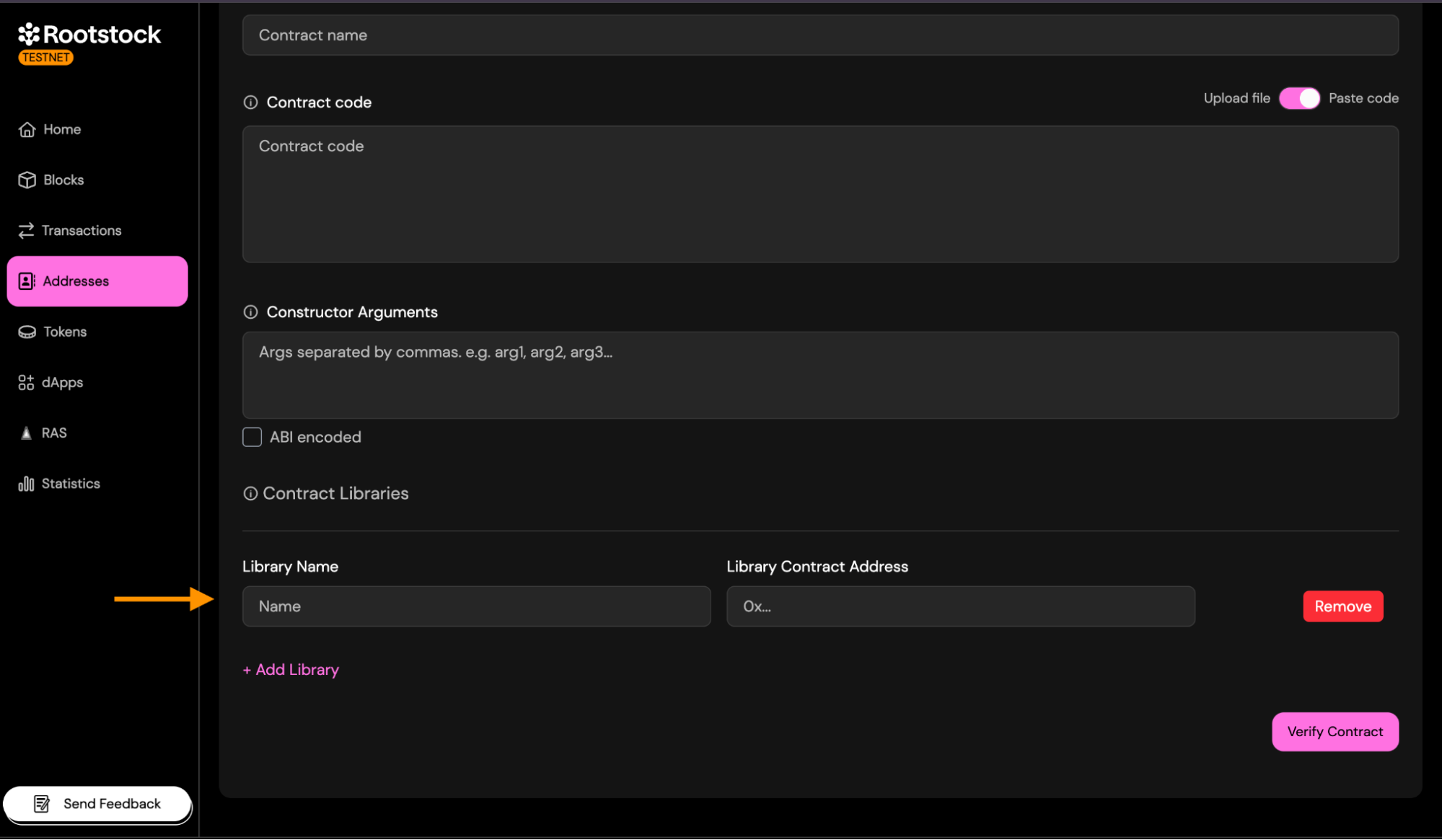
Libraries: If your contract links external libraries add each required library.
Provide:
- Library Name.
- Library Contract Address (the address where the library was deployed).
This step is required only if the compiled bytecode contains libraries.
2. Multiple Files
The Solidity (Multiple Files) method is designed for more complex contracts that use imports, have multiple .sol files, or cannot be flattened safely. This method allows you to upload all your Solidity source files exactly as they exist in your project.
Only the parts that differ from Single File are described below.
- Sources Files: Upload all Solidity files required to compile your contract, preserving the original folder structure.
You can:
- Drag and drop multiple .sol files.
- Upload an entire folder containing your contracts.
- Combine both approaches if needed.
Important rules:
- Every imported file must be included.
- Filenames must match exactly (case-sensitive).
- Folder structure should reflect your project layout.
- Do not flatten the files — this method expects multi-file compilation.
During verification, the explorer will reconstruct the compilation environment using the files you provide.
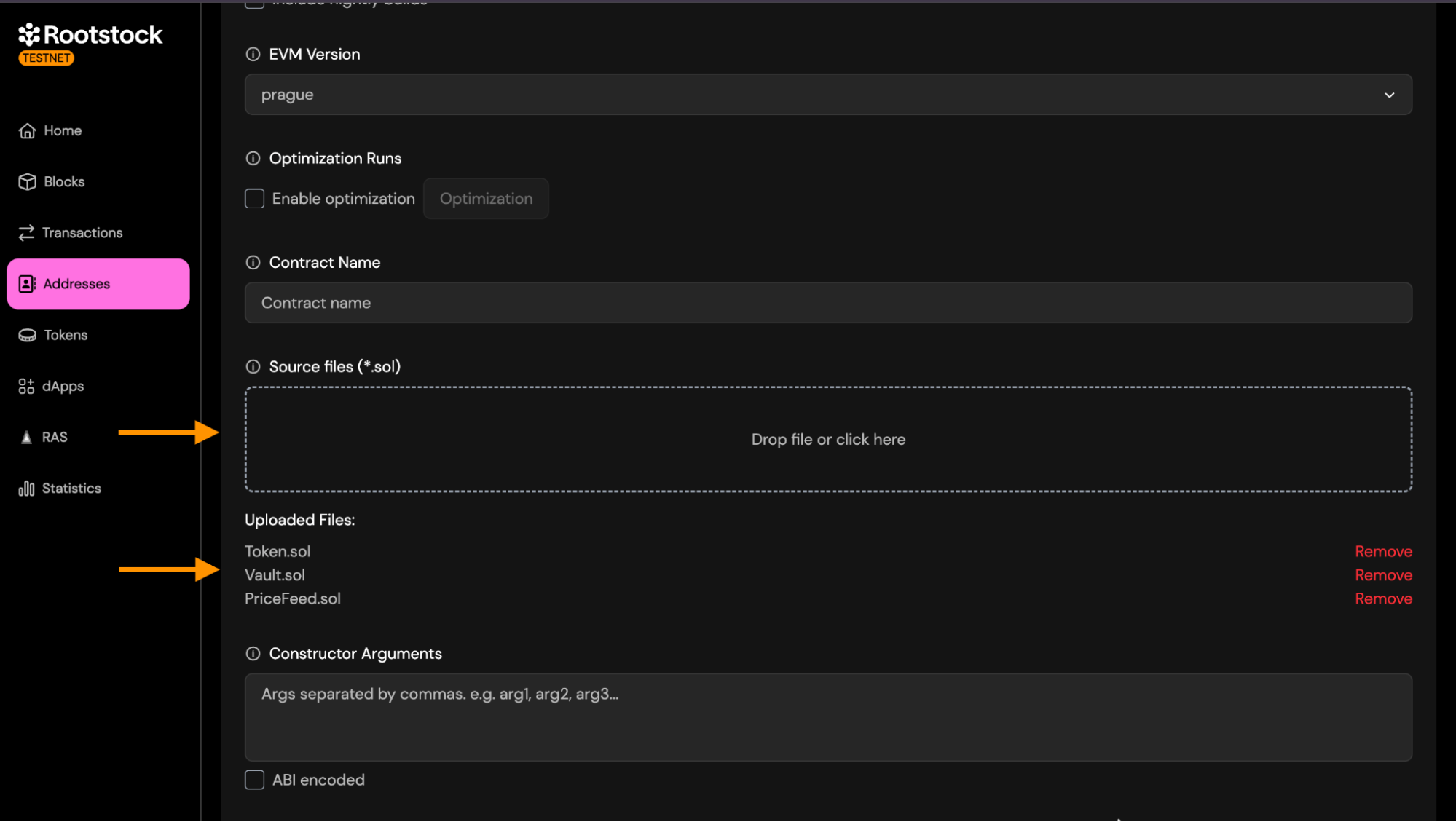
- Other Settings: All other fields (compiler version, EVM version, optimization, contract name, constructor arguments, libraries.) work exactly the same as described in the Single File Verification section.
3. JSON Standard
The Standard JSON Input method is the most reliable and exact verification approach. It reproduces the full Solidity compiler configuration used during deployment by providing a complete standard-json object, exactly as consumed by solc --standard-json.
This method is strongly recommended for:
- Projects compiled with Hardhat, Foundry, Truffle, or custom build scripts.
- Contracts with complex dependency structures.
- Projects where preserving metadata (AST, settings, compiler options) is essential.
- Ensuring a byte-for-byte deterministic match with the deployed bytecode.
The Solidity (Multiple Files) method is designed for more complex contracts that use imports, have multiple .sol files, or cannot be flattened safely. This method allows you to upload all your Solidity source files exactly as they exist in your project.
How to Generate Standard JSON Input:
Hardhat:
npx hardhat compile --show-stack-traces
Then locate the standard-json file inside Hardhat’s internal
artifacts/build-info/*.json.
Foundry:
forge build --extra-output-files solc-input
Foundry will export solc-input.json into
out/.
-
How to Extract the Standard JSON Input:
After generating the file (from Hardhat or Foundry):
- Open the JSON file that was produced.
- Inside it, locate the field named "input".
- Copy everything inside the input object — this is the actual Standard JSON Input expected by the verifier.
- Paste it into a new file, and save it using the contract's name.
- Your file should look similar to the following structure:
{
"language": "Solidity",
"sources": {
"Token.sol": {
"content": "..."
},
"PriceFeed.sol": {
"content": "..."
},
"Vault.sol": {
"content": "..."
}
},
"settings": {
"optimizer": {
"enabled": false,
"runs": 200
},
"outputSelection": {
"*": {
"": [
"ast"
],
"*": [
"abi",
"metadata",
"devdoc",
"userdoc",
"storageLayout",
"evm.legacyAssembly",
"evm.bytecode",
"evm.deployedBytecode",
"evm.methodIdentifiers",
"evm.gasEstimates",
"evm.assembly"
]
}
},
"remappings": [],
"evmVersion": "london"
}
}
Standard JSON Input File (*.json)
Upload a single .json file containing the full Standard JSON Input object used to compile your contract.
This file typically includes:
- language
- sources (all .sol files embedded with their contents)
- settings such as:
- optimizer configuration
- remappings
- metadata settings
- output selection
- evmVersion
- libraries (if linked during compilation)
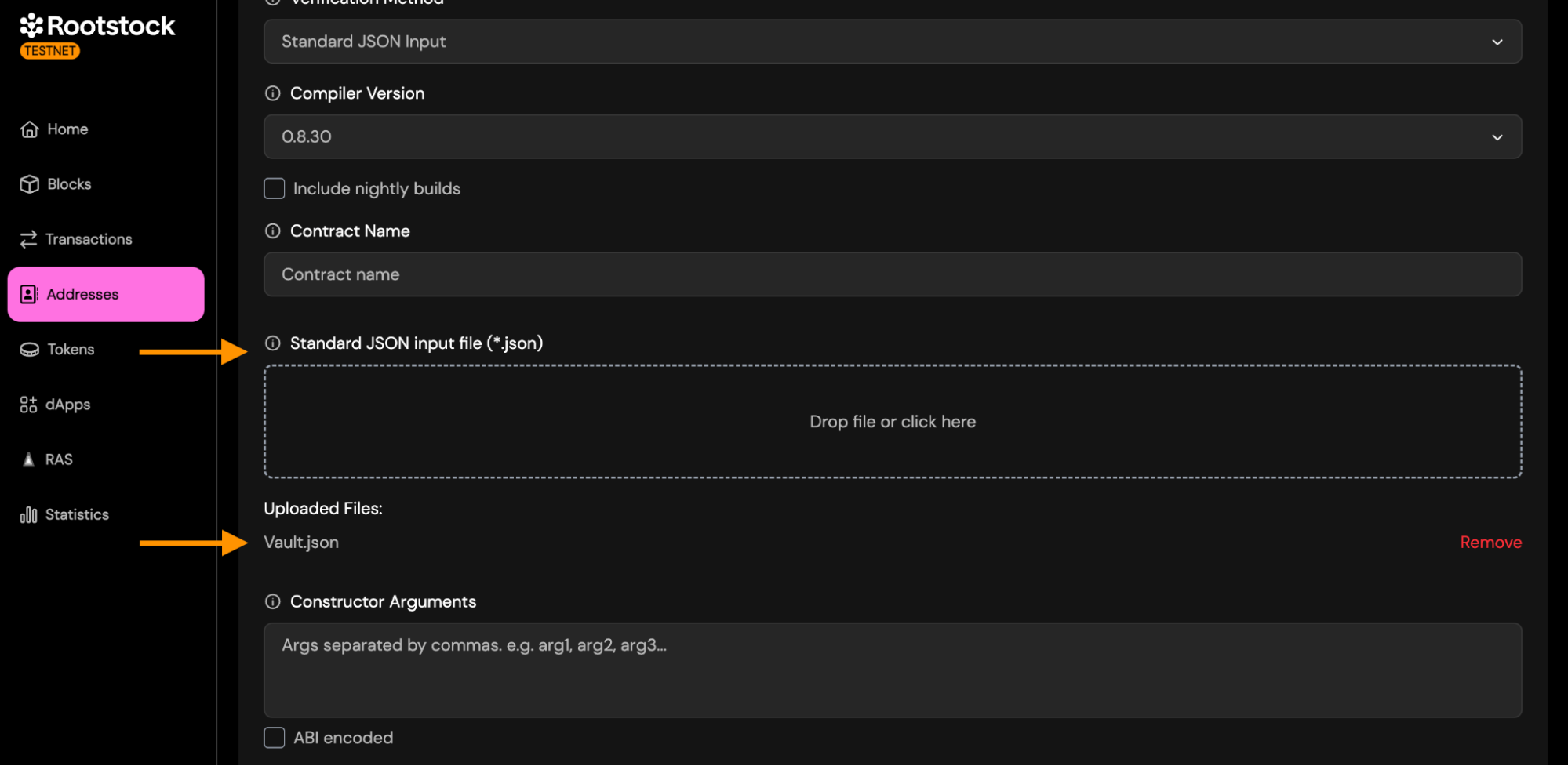
- Other Settings: All other fields (compiler version, optimization, contract name, constructor arguments, libraries.) work exactly the same as described in the Single File Verification section.
4. Hardhat Verification
Select Hardhat as your verification method to verify contracts directly from your Hardhat project. This method does not require uploading files through the interface — instead, verification is performed using the Hardhat CLI.
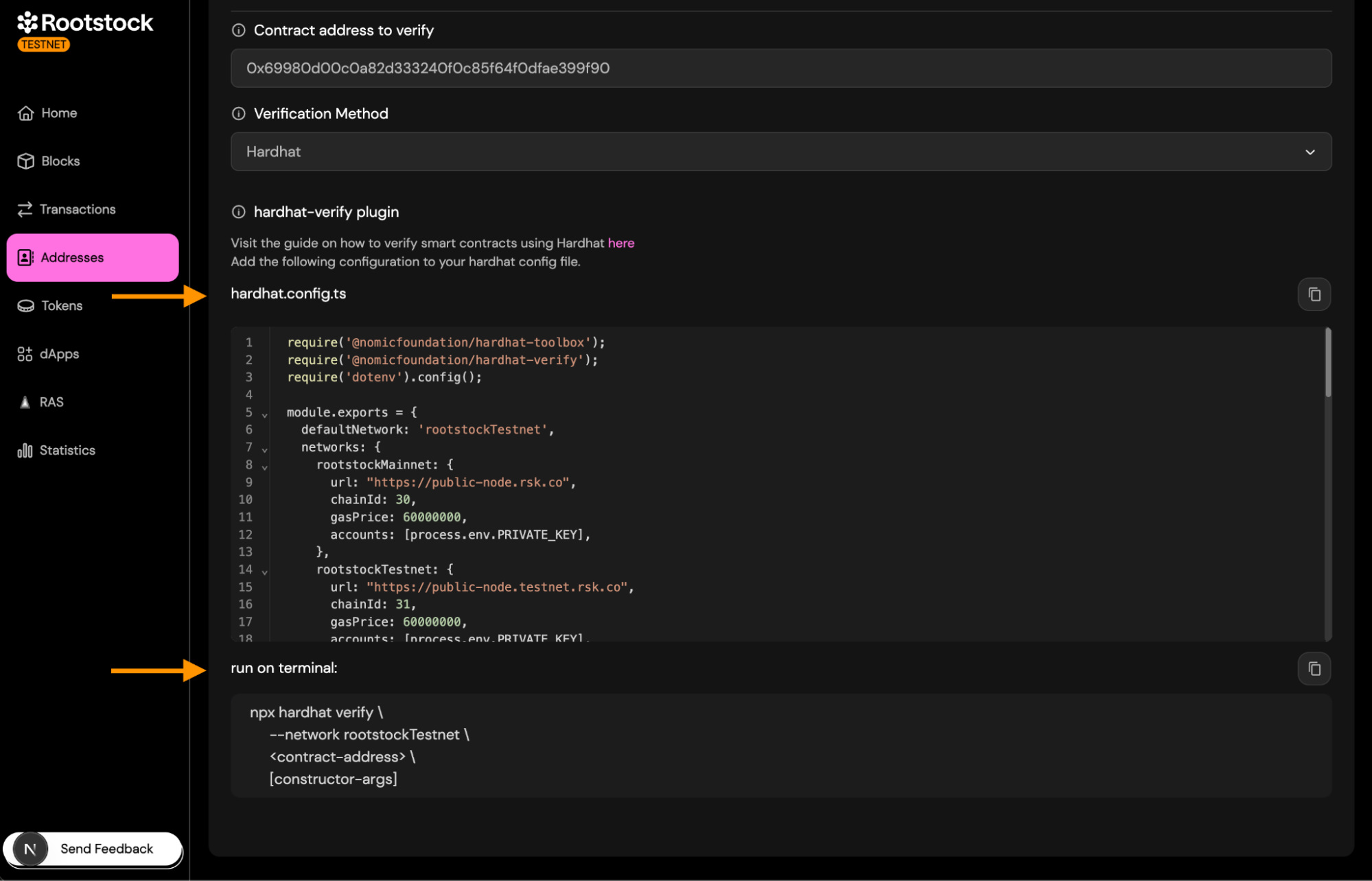
Copy the configuration snippet into your hardhat.config.ts file.
This snippet includes:
- The Hardhat Verify plugin
- Rootstock Testnet/Mainnet RPC URLs
- Chain IDs
- Account setup for signing requests
Make sure your PRIVATE_KEY is defined in your .env file.
Run the verification command in the terminal:
npx hardhat verify \
--network rootstockTestnet \
<contract-address> \
[constructor-args]
Replace:
<contract-address>with your deployed contract address[constructor-args]with constructor parameters (if any)
Once it completes successfully, your contract will be verified on the Rootstock Explorer.
To see a detailed explanation on how to verify contracts using Hardhat, visit here
5. Foundry Verification
Select Foundry as your verification method to verify contracts using the forge verify-contract command.
This method integrates Foundry directly with the Rootstock Explorer’s verification API, allowing you to verify a deployed contract from your local environment.
Run the verification command in the terminal:
forge verify-contract \
--chain-id 31 \
--watch \
--compiler-version v0.8.24 \
--verifier custom \
--verifier-url https://explorer-testnet-api-v3.plattie-qa.iovlabs.net/api/v3/etherscan \
<contract-address> \
<contract-file>:<contract-name>
Replace:
<contract-address>→ the deployed contract address.<contract-file>→ path to the Solidity file inside your project.<contract-name>→ name of the contract inside that file.
Once the command finishes, your contract will appear as Verified on the Rootstock Explorer.
To see a detailed explanation on how to verify contracts using Foundry, visit here
Submit and Validate
Once you have entered all the details, click "Verify Contract".
-
Expected statuses: The verification status will change from "Pending" to "Success" or "Failure".
-
On successful status:
a. You will see the
Verifiedbadge on the contract page.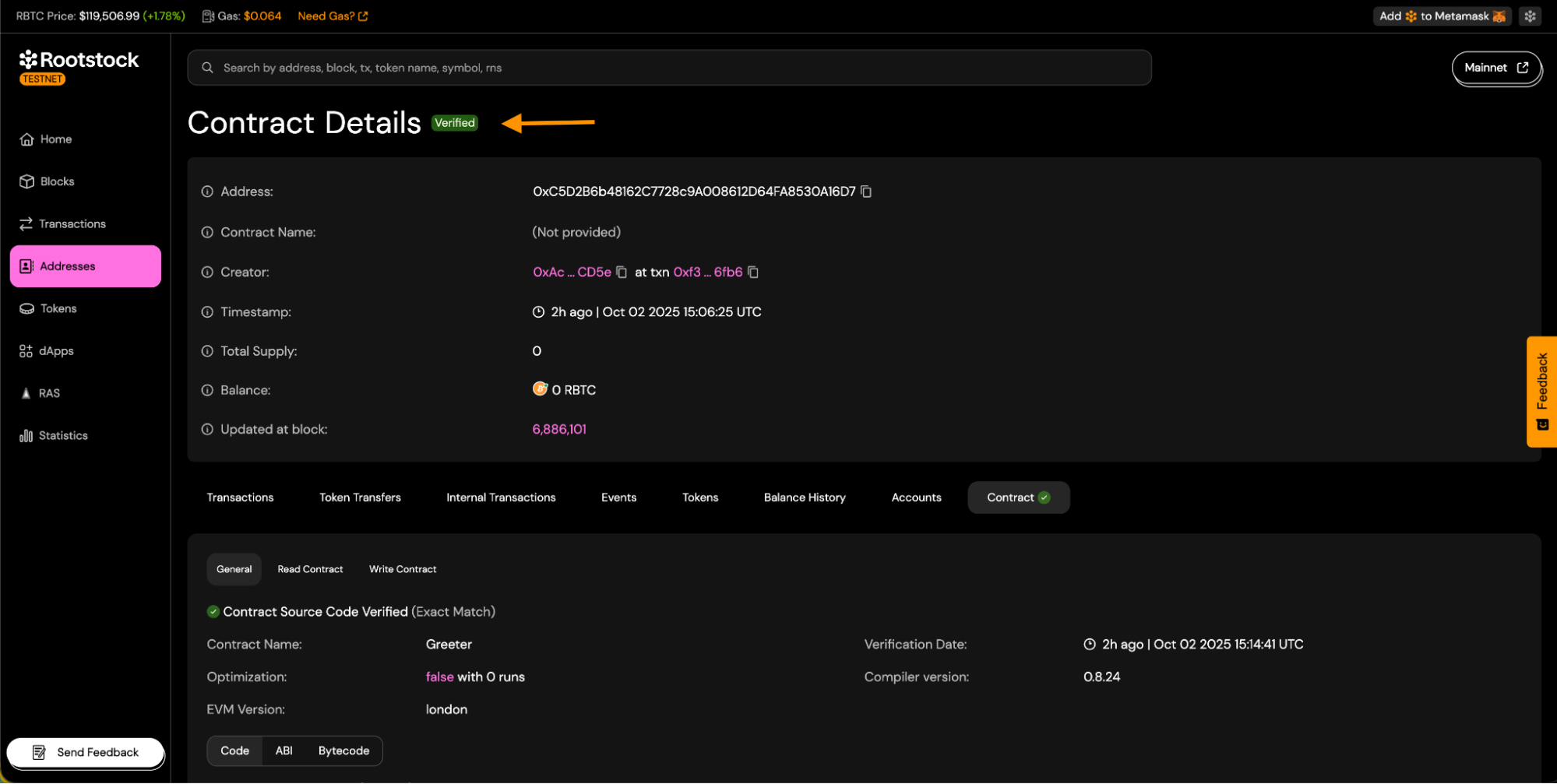
b. Source code tabs will be visible.
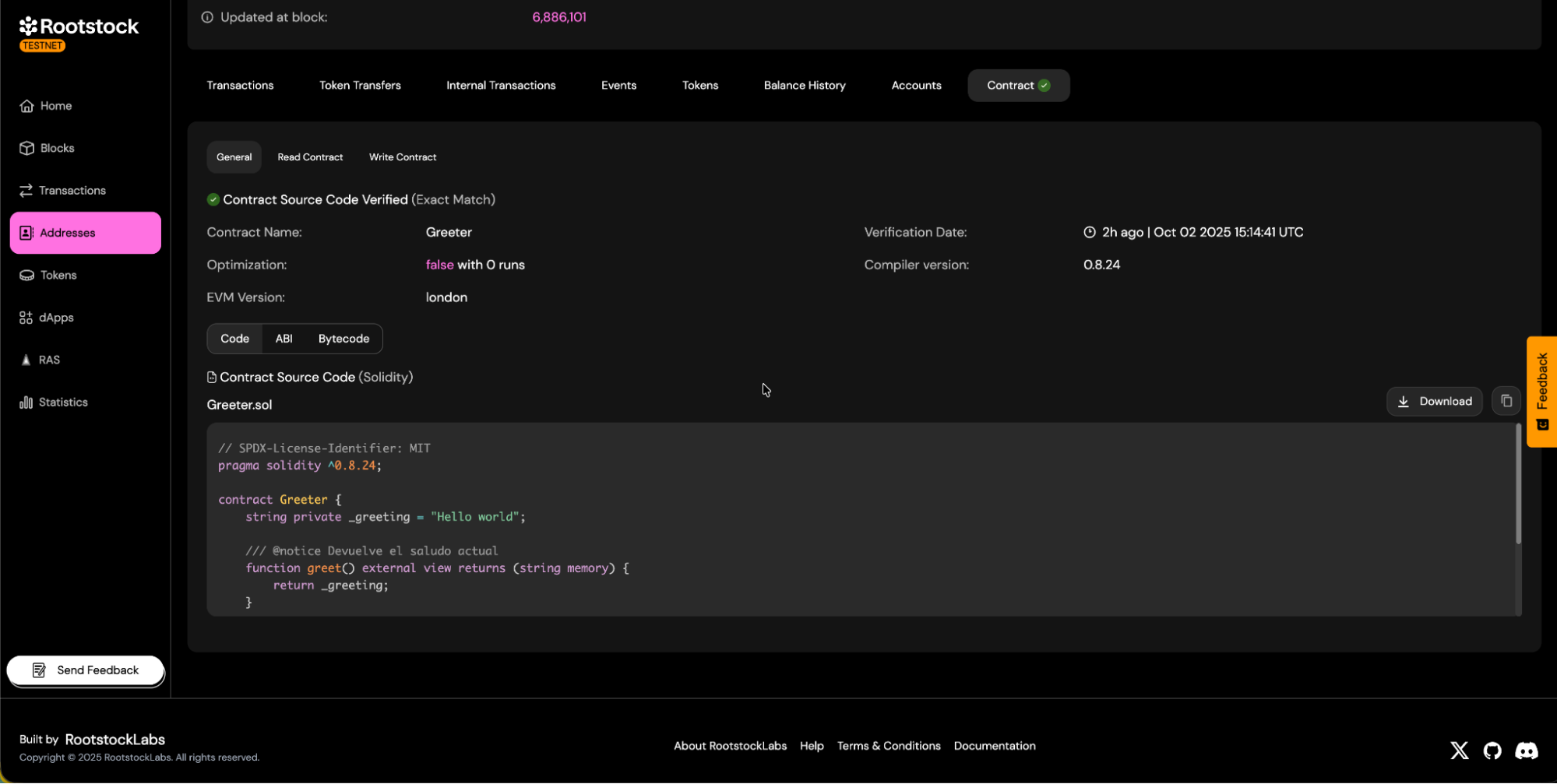
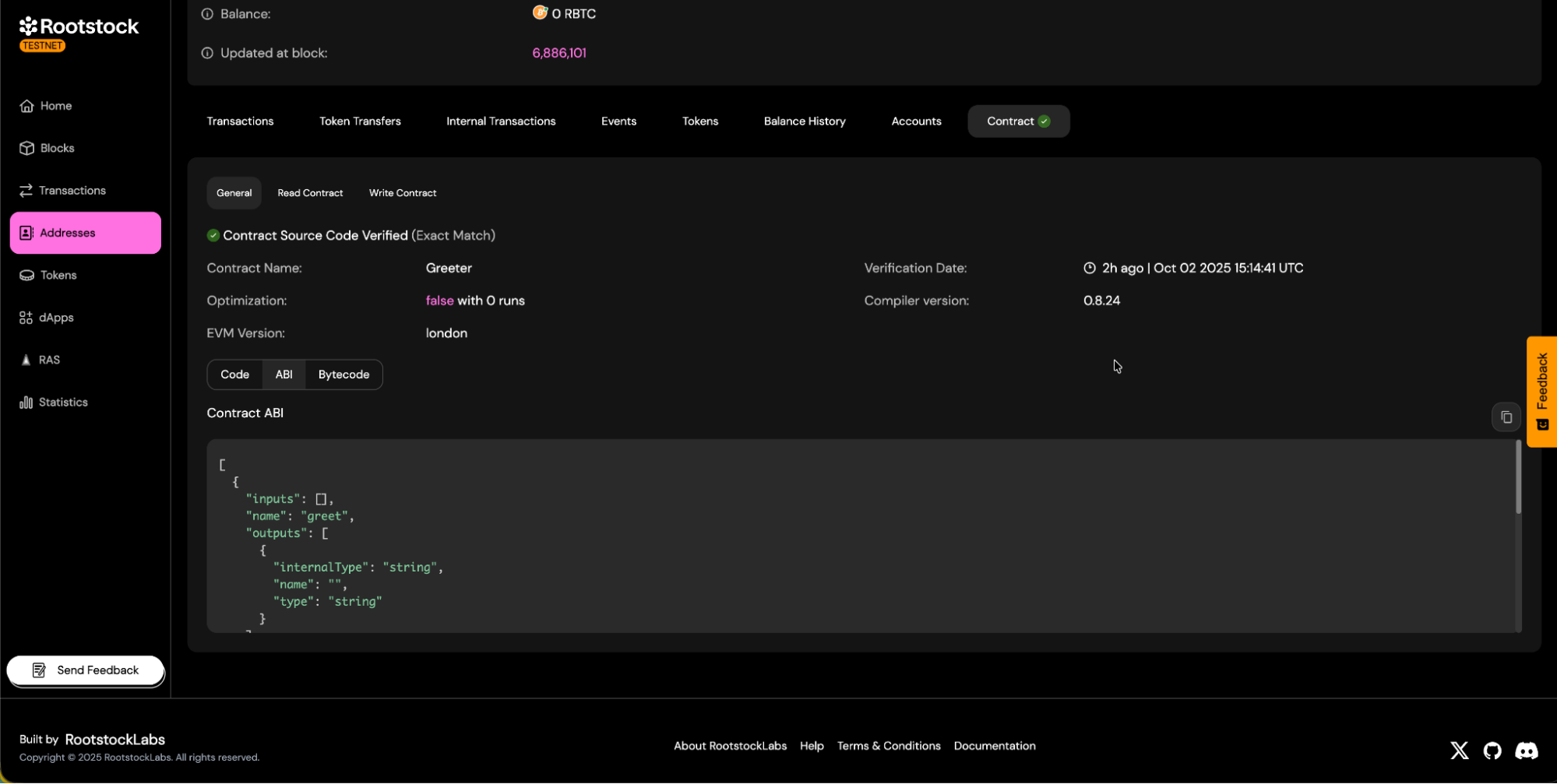
c. You will be able to download the contract ABI.
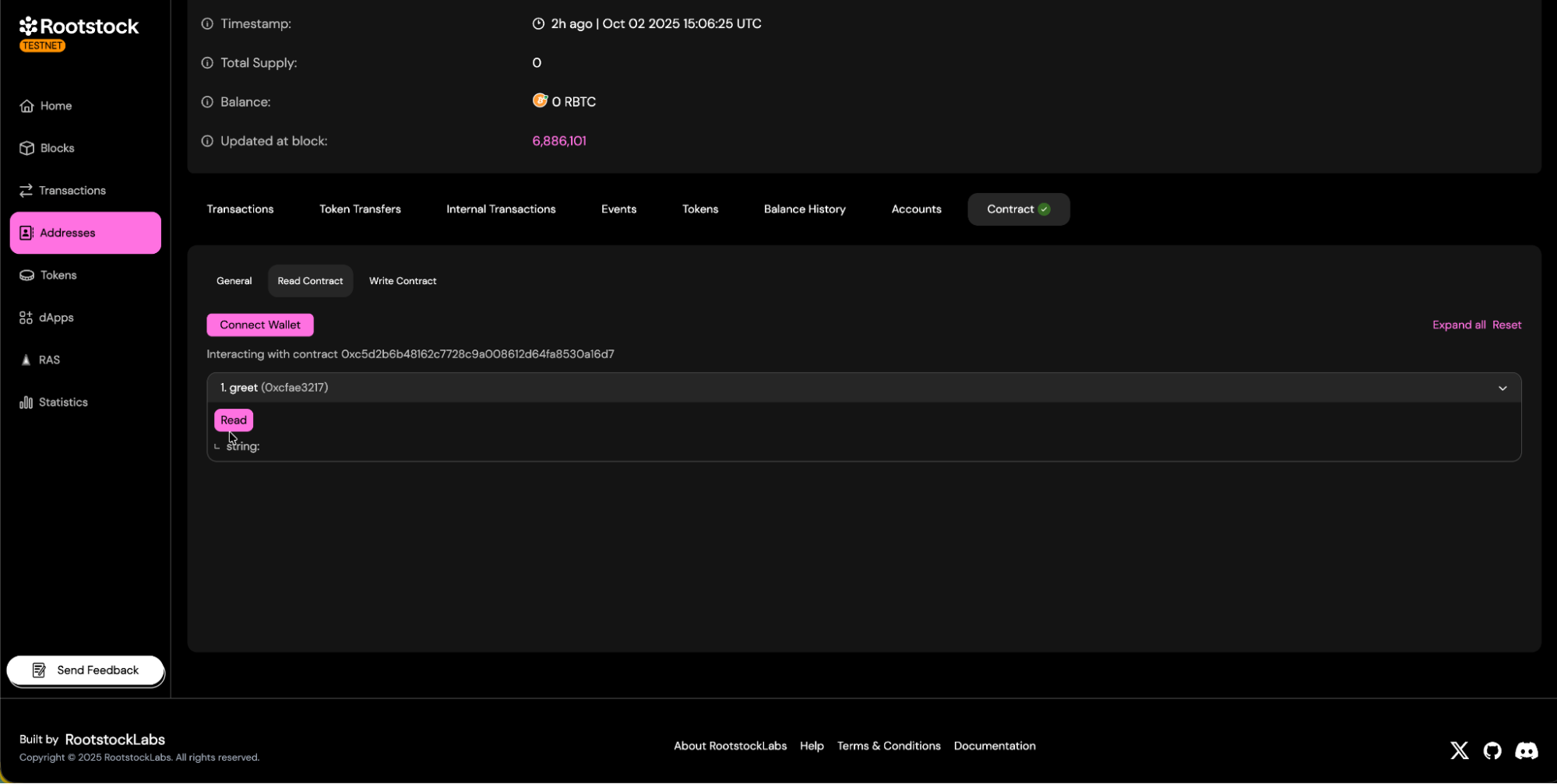
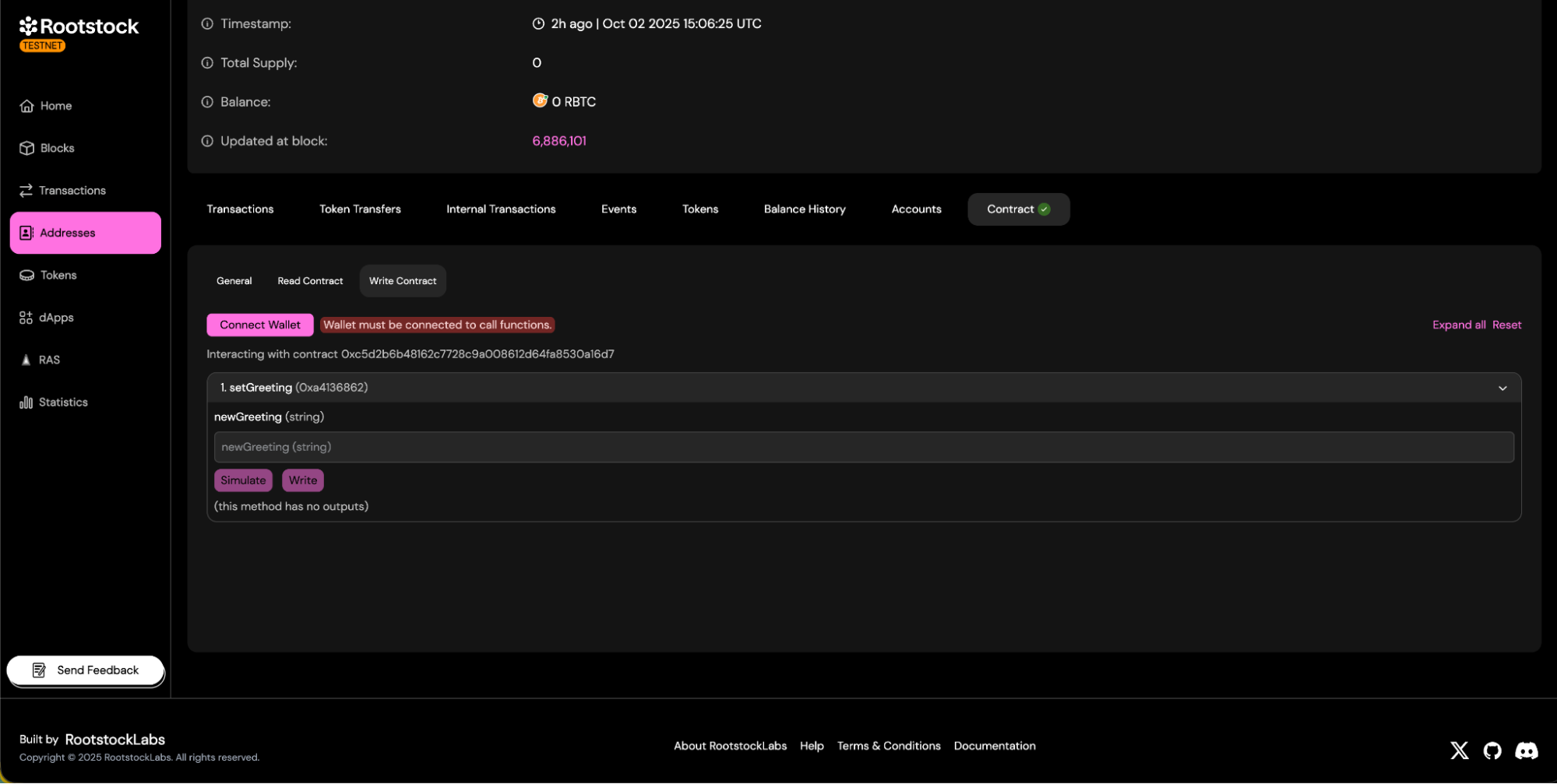
d. Contract read and write panels will be available.
- Read Methods:
- Write Methods:
- Read Methods:
Troubleshooting
- Here are some common errors and their solutions:
- Confirm the exact Solc version used to compile your contract.
- Retrieve the version from your compilation artifacts.
- Verify the precise encoding, order, and types of your constructor arguments.
- Ensure library names match bytecode placeholders.
- Add the correct deployed addresses for each library.
- Align the number of optimization runs with your compilation settings.
- Consider using the Standard JSON verification method to avoid path or flattening issues.
- Verify the implementation contract.
- Note any proxy-aware UI (if available) and how to link it.
💡 Tip: If verification keeps failing, try matching the compiler settings directly from your Hardhat or Foundry build artifacts.
Resources
- Verify smart contracts using Blockscout or Hardhat Plugin